
In September 2022, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) levied a combined penalty of more than $1.1 billion on 16 Wall Street firms. Prominent brokerages such as Goldman Sachs and Barclays featured on the list.
What were they charged of?
Failure to comply with various provisions of the Market Access rule.
Between May and July 2017, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and other self-regulatory organizations penalized the likes of Deutsche Bank Securities, Citigroup Global Markets Holdings, and J.P. Morgan Securities LLC to the tune of a whopping $4.8 million. The three organizations neither denied or accepted the charges. They settled the sanctions for failure in preventing erroneous trading orders, among other non-compliance issues.
In December 2014, the SEC brought Morgan Stanley under the scanner for not having adequate safeguards to limit potential risks posed by its access to the markets. Morgan Stanley also fell short of conducting adequate reviews of the effectiveness of its controls.
These events highlight the continued need to build more transparent pre-trade monitoring tools for the securities market landscape, given how unauthorized access and rigged events shake the foundation of an otherwise orderly functioning U.S. securities market.
Market Access Rule or SEC Rule 15c 3-5
It is in this context that the SEC incorporated the Market Access Reg or Rule 15c3-5 in 2010, as part of the Securities Act of 1934.
The Market Access Rule requires that broker-dealers establish, document, and maintain adequate risk management controls and supervisory procedures that are designed to manage the risks (financial, regulatory, and operational) associated with market access.
Brokerage firms or broker-dealers operating in the capital markets and exchange-traded derivatives (ETD) markets have a mammoth responsibility to establish adequate ‘in-line’ checks and controls around their electronic order flow and market access.
In this article, we revisit Rule 15c3-5 for its worth and analyze its significance in the current securities and capital markets landscape. We explore its applicability, the consequences of non-compliance, the role of a robust Order Management System (OMS) in improving compliance, and how Ionixx can help meet and maintain compliance with robust technological frameworks.
Tracing The Origin and Evolution of Rule 15c3-5 or The Market Access Rule
In 2010, following the NYSE “flash crash”, the SEC realized the absolute need to gatekeep pre-trade entries in order to avert and manage potential risks.
The flash crash set the alarm bells ringing of an ominous systemic collapse, what with the NYSE falling like a pack of cards, all attributed to a single erroneous sell order. It was a curious case of a missed fat-finger check.
The SEC designed the rule to “reduce the risks faced by broker-dealers, as well as the markets and the financial system as a whole, as a result of various market access arrangements, by requiring effective financial and regulatory risk management controls reasonably designed to limit financial exposure and ensure compliance with applicable regulatory requirements to be implemented on a market-wide basis.”
SEC.gov
Relevance Today: Why All the Hand-Wringing by SEC And FINRA?
The volume of electronic trading that we’ve seen in the last few years plus the rising number of high-frequency traders have brought back the focus on the Market Access Rule.
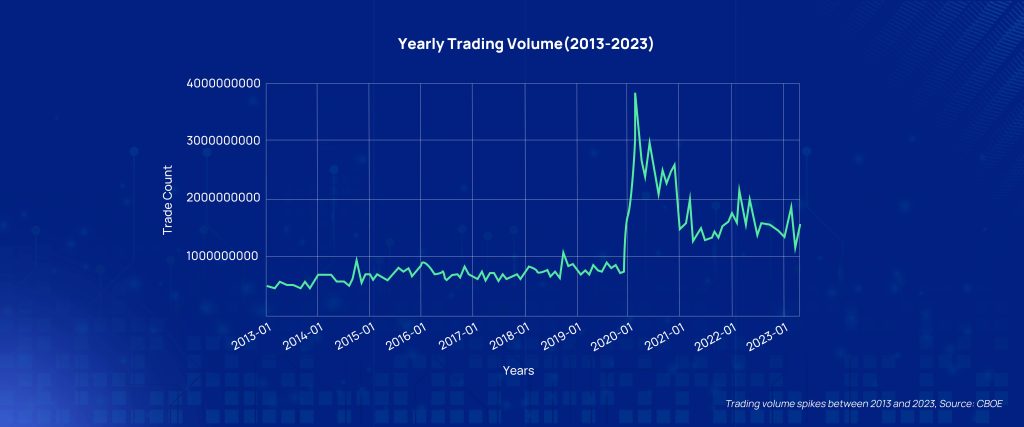
Trading volume spikes between 2013 and 2023, Source: CBOE
There are two key factors that drive the relevance of Rule 15c3-5 in the current securities landscape.
- The burning need to establish appropriate credit and capital thresholds: It has become crucial to keep a tab on credit and capital limits. Broker-dealers are expected to ensure that their customer limits are not just deemed “reasonable” but are part of a comprehensive framework that can be demonstrated to regulators.
Questions, while they vet potential broker-dealer firms, would be:
- Has the firm established a well-thought-out methodology for setting credit limits?
- Have all the factors and parties involved been taken into consideration?
- Has the firm documented supervisory procedures that guide electronic trading desk personnel to decide whether or not to increase customer trading thresholds?
- Is the firm using a one-size-fits-all approach when it establishes limits for different customers and businesses?
- Is the firm equipped with a strong due diligence system that can prevent circumvention of market access compliance?
- The need to control erroneous and duplicative orders: Electronic connectivity and automated trading in the capital markets, including the use of algos, are not new. However, e-trading has been expanding, not only in the speed and sophistication of the computer models themselves but also through increased volumes and expansion to new asset classes and markets. This presents an inherent catch — The possibilities of erroneous or duplicative orders are on the rise. Brokerage firms are obligated to identify these orders, within reason, and ensure their legitimacy and compliance with other obligations before routing or executing them.
To discourage duplicative or erroneous trades, the Market Access Rule imposes certain obligations on broker-dealers. Here’s how:
- Risk controls: Broker-dealers are expected to include pre-trade checks on order parameters such as order size, price thresholds, and message rates, as well as post-trade surveillance.
- Financial risk management: Broker-dealers must establish financial risk management controls to monitor their customers’ trading activity and prevent them from exceeding preset credit or capital thresholds.
- System safeguards: Broker-dealers are mandated to have robust system safeguards in place to ensure the security and integrity of their market access systems.
- Order execution monitoring: The rule also requires broker-dealers to regularly monitor their customers’ order executions to identify any patterns of potential duplicative or erroneous trades.
- Recordkeeping requirements: Broker-dealers are obligated to maintain records related to their compliance with the Market Access Rule, enabling regulators to review their risk management and control systems.
Realizing the uncontrolled proliferation of electronic trading desks, the SEC and FINRA stay vigilant of all the possible risks that erroneous trade orders or unrestricted market access could bring.
Potential Risk Areas of Poor Pre-Trade Monitoring
Unauthorized Access And Operational Risks
Let’s say a trader gains unauthorized market access through a brokerage firm’s trading system and executes large trades on behalf of the firm, without appropriate risk management controls. These trades result in substantial losses for the firm. This suggests that the lack of a stringent onboarding mechanism with appropriate pre-trade controls may unintentionally pave the way for unauthorized trading activities and erroneous trade orders. This could potentially lead to widescale financial losses, harming the integrity of the markets. This also opens the door for potential rogue trading, unauthorized or excessive risk-taking, or fraudulent activities that can harm both the firm and its clients.
Erroneous Entries and Systemic Risks
If a trader mistakenly enters an order to buy 10,000 shares instead of the intended 1,000 shares due to manual input errors or system glitches, the trade executes at a significantly higher price. This results in substantial losses for the firm or its clients. Submission of erroneous manual orders has the potential of causing systemic risks affecting the performance of the entire market or even market risks, such as plummeting of interest rates or equity/commodity prices due to unfiltered access to the market.
Legal And Regulatory Consequences
With poor pre-trade checks or the lack of them, firms may increase the opportunities for regulatory bodies to clamp them down with fines, penalties, legal recourse, or suspension/revocation of licenses or permissions to operate in the financial markets. These consequences not only impact the violating firm but can also erode market confidence and reputation.
Market Integrity Factors
Compliance with market regulations is crucial for maintaining market integrity and investor protection. Non-compliance undermines the overall fairness and transparency of the markets, potentially leading to market manipulations, insider trading, or other fraudulent activities. The reputation and trust of investors and other market participants may be compromised, negatively impacting market liquidity and efficiency.
Before Rule 15c3-5: A Look Into the Pre-Trade Monitoring
Before the enforcement of the Market Access Rule, broker-dealers and trading firms had limited regulations for implementing pre-trade risk monitoring and management controls. Around the same time, the prominence of algorithmic and high-frequency trading increased. This naturally led to unprecedented trade spikes with trading strategies that relied on high-speed computer algorithms.
The absence of clear regulations meant that trades weren’t thoroughly checked in the pre-market entry phase. This caused either duplicate trades or errored trades that involved a lot of manual intervention while rectifying them.
Significant Changes Instituted by The Market Access Rule
The Market Access Rule introduced comprehensive regulations for market access and pre-trade onboarding practices. It aimed to address concerns by mandating risk controls, establishing uniform standards, and enhancing the overall stability and integrity of the US securities markets. Here is a snapshot.
- Enforcement of risk constraints: Enforcing financial risk constraints on the customer’s activity (i.e., credit limits, position concentration limits, and the like).
- Placing a cap on credit and capital: Preventing the entry of orders that exceed appropriate pre-set credit or capital thresholds in the aggregate for each customer and the broker-dealer.
- Check on erroneous orders:
- Preventing the entry of erroneous orders, by rejecting orders that exceed appropriate price or size parameters, on an order-by-order basis or over a short period of time, or that indicate duplicative orders.
- Preventing the entry of orders unless there has been compliance with all regulatory requirements that must be satisfied on a pre-order entry basis;
- Preventing the entry of orders for securities that the broker-dealer or customer is restricted from trading;
- Placing access controls: Restricting market access technology and systems to authorized persons; and
- Post-trade surveillance and reporting: Assuring appropriate surveillance personnel receive immediate post-trade execution reports.
Why Is Revisiting The Rule Now A Priority: The Stakes
The need to revisit this rule is relevant now with the capital markets landscape becoming increasingly digitized and complex. Given how proactive gatekeeping can weed out potential vulnerabilities in electronic trading systems, this helps safeguard against disruptive events that could have severe systemic implications.
Periodic Assessment and Certification
Pre-trade monitoring is a crucial component in gaining control and visibility of the entire trading lifecycle, and that makes periodic assessments of risk factors and supervisory procedures a must. This is also why the rule mandates that broker-dealers conduct annual assessments. This helps proactively gauge the effectiveness of the risk management controls.
Additionally, the Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) of the broker-dealer will be required to certify annually that the risk management controls and supervisory procedures comply with the requirements of the Rule on the basis of the periodic review.
SEC.gov
Hence, SEC Rule 15c3-5 stands as a paramount measure, shaping the very foundation of the trading market, making it indispensable for all its participants.
How Can You Prepare for Rule 15c3-5 Compliance?
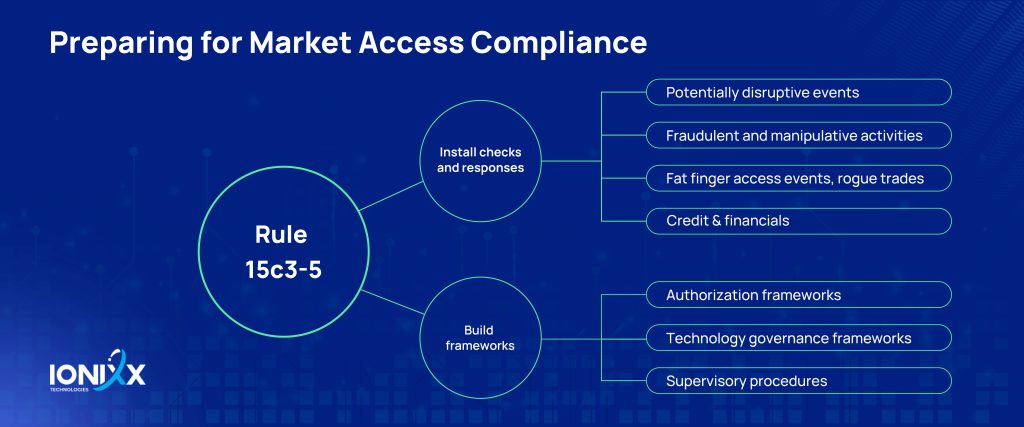
Asset managers and buy-side firms looking to get a handle on their compliance game should take the following pointers to heart.
- Staying nimble for technology rehauls: An agile infrastructure that quickly integrates with new technology can help implement changes swiftly. If you are looking to stay compliant with the Market Access rule, you should revamp your existing OMS and EMS systems to keep pace with changing regulations. Additionally, it’s also crucial that you periodically revisit market access agreements with existing third parties.
- Investing in staff training: In terms of training personnel on changing technology frameworks, you will probably need to invest in training and upskilling broker-dealers on a going-forward basis; given the new or expanded responsibilities.
- Leveraging a modern OMS: Investing in a dynamic Order Management System (OMS) serves as a value enabler for enhancing compliance with Rule 15c3-5, empowering broker-dealers to implement robust risk management controls throughout the trading lifecycle. OMS platforms enable broker-dealers to establish effective pre-trade checks, post-trade monitoring, and analytics. This keeps errors to a minimum, thus ensuring compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.
Does The Rule Affect Clearing and Settlement?
The Market Access Rule also has implications for broker-dealers providing clearing services.
Why?
If an unauthorized trade is already in the books and records, there is a need to ensure proper book-keeping methods and transaction record updates when reverting or fixing erroneous trades that should have never happened in the first place.
Unauthorized trades can result in the need for labor-intensive manual intervention processes in the post-trade system. For example, the cancel trade feature is typically used if an order is found to be erroneous or duplicated. This is a time-consuming process that slows down the entire system, adding man-hours in back-office operations.
If broker-dealers can filter orders through effective pre-trade checks before it becomes a trade, it can help maintain the integrity of post-trade settlement systems.
The Role of a Robust OMS in Improving Rule 15c3-5 Compliance
Order Management Systems (OMS) play a vital role in streamlining trading activities and ensuring compliance with Rule 15c3-5. Advanced OMS platforms offer risk management tools that brokerage forms use to maintain controls over order entries, order routing, and execution.
Listed below are a few key aspects that an OMS platform helps broker-dealers with:
- Proactive gatekeeping: They actively gatekeep orders by maintaining a log of their activities through their trade lifecycle. Through a proactive approach, OMS platforms help spot any suspicious activity or regulatory breaches.
- Enabling inherent risk checks: Broker-dealers enforce risk controls by integrating pre-trade risk checks into the OMS workflow, at the point of order entry. These checks include limits on order size, trading thresholds, order routing restrictions, and customer-specific risk requirements.

- Automation for low touch: Automated pre-trade checks embedded within an OMS significantly reduce the chances of erroneous or disruptive trades entering the market and enhance compliance with Rule 15c3-5. Additionally, as trade volumes continue to increase, automation helps keep prevent severe outages, which are characteristic of manual processing systems.
- Facilitating real-time monitoring: Modern OMS tools facilitate real-time monitoring of trading risk exposures, enabling broker-dealers to implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies promptly. By leveraging efficient reporting and analytics capabilities, OMS systems offer insights into trading patterns, supported by detailed transaction records, and aid in identifying potential risks and anomalies.
Closing Thoughts
In an era dominated by algorithmic trading, automated systems, and generative AI, the need to comply with the Market Access Rule is a no-brainer. Compliance issues can negatively impact your bottom line; the best way to get through these pitfalls is by using pre-trade risk and compliance monitoring software.
We help you leverage the best-in-class technology frameworks and tools to enhance your compliance and risk mitigation systems. It’s in your best interest to take a proactive approach to pre-trade monitoring.
Act now and stay compliant, ahead of your competition.


