The US and Canada want to lower securities settlement from T+2 to T+1 by mid-2024. Thus, trade settlement must start immediately. The European Union’s Central Securities Depositories Regulation (CSDR) is also driving middle-office upgrades and automation to reduce settlement failures and fines, which affect industry players’ profitability.
Aside from regulatory issues, there is a desire to minimize TCO, especially given recent market volatility. Thus, middle office functions must be automated and improved.
Investment firms must also build new post-trade infrastructure to accommodate the next generation of cryptocurrency traders. These assets require same-day settlement. It’s a real-time necessity from the middle to the back office. Financial institutions are increasingly using digital assets in portfolios to ease post-trade processing.
Enhancing the middle office service to acquire a worldwide perspective of t+0 settlement data or a cross-asset view of equities and fixed-income holdings can lower TCO.
What is Middle-Office System?
The Middle Office constitutes a pivotal division within financial institutions, like investment banks and asset management firms, assuming a vital role in trade lifecycle and risk mitigation. Positioned between the front office (trading desks) and back office (settlement and accounting) functions, it undertakes diverse responsibilities encompassing trade validation, risk management, trade support, and post-trade processing.
Within the trading context, the middle office services assume pivotal roles, including:
Trade Validation: It is the process of verifying the trade executed by the front office is accurate and adheres to the regulatory standards and internal protocols.
Trade Support: Providing operational support to the Front Office, including resolving trade-related issues and inquiries.
Risk Management: Evaluating and effectively managing the risks associated with trading activities, such as credit risks, market risks, and operational risks.
Trade Confirmation: Confirming trade details with counterparties to ensure both parties agree on the terms of the trade.
Trade Settlement: Facilitating the settlement process, which involves the exchange of cash and securities to finalize the trade.
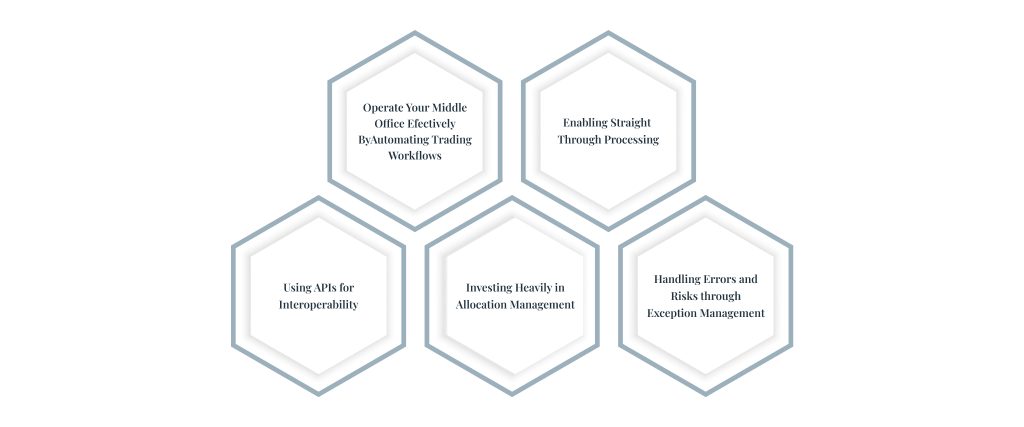
What Are the Features That the Middle-Office System Needs?
Trade Automation:
Middle office trade automation entails using the latest technology and software systems to automate trade processing, validation, and management, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. It encompasses various facets of trade lifecycle management within financial institutions, aiming for seamless operations.
Trade automation finds application in several critical areas within the middle office process, including:
Automated Trade Validation and Enhancement: To ensure accuracy and completeness, automated systems can check incoming transaction data against predefined rules and market conventions. The enrichment process can also automatically add missing information or correct inaccuracies in trade data.
Regulatory Reporting: Accurate and timely reporting of transaction data is essential to comply with numerous financial requirements. Automation can help in report generation and submission to the appropriate regulatory bodies.
Middle office Risk Management: Using real-time monitoring and analysis of trading positions and exposures, automated risk management systems in the middle office can assist in identifying and mitigating potential risks related to trades.
Straight-Through Processing (STP): STP refers to the seamless automation of the entire trade lifecycle, from order initiation to settlement, without manual intervention. Implementing STP reduces operational costs and processing times while improving accuracy.
Reconciliation: Automated reconciliation systems can compare data from several platforms or systems to guarantee correctness and consistency, especially for data pertaining to trade.
Allocation Management:
Allocation Management is a crucial part of the middle office system, as it allocates a large block trade across multiple client accounts or funds. The block may get higher in number due to the spike in the trade volume. So, it is important to spend on allocation management, and it should be automated for effective allocation.
Exception Management:
In middle office trade operations, exception management entails discovering, tracking, and resolving trade-related issues. These exceptions can occur for a variety of reasons, including data errors, trade validation issues, settlement delays, or regulatory noncompliance. Effective exception management is critical for guaranteeing seamless trade processing and lowering operational risks in financial institutions.
Interfaces and Connectivity:
In the financial services industry, the middle office often acts as a critical link between the front office and the back office. To fulfill its responsibilities effectively, interfaces and networking solutions let the middle office share data and information between systems and divisions. Interfaces and connectivity solutions streamline transaction processing, risk management, and compliance monitoring. Here are the key middle office interfaces and connectivity:
Trading System Interfaces: The middle office needs real-time trade data from the front office’s trading systems. The middle office software can check and enrich trade information, match deals with counterparties, and monitor trade execution using APIs.
Market Data Interfaces: The middle office utilizes the most recent market information for trade valuation, risk calculations, and decision-making via interfaces with market data providers that supply prices, volumes, and other relevant data.
The middle office receives real-time risk data, exposure analysis, and stress testing findings from risk management systems. These interfaces enable the middle office to identify and manage front-office trade risk.
Compliance and Regulatory Interfaces: The middle office interfaces with regulatory reporting systems to comply with regulatory compliance and internal policies. These interfaces monitor trades for breaches and enable rapid regulatory notification.
Interfaces with counterparties and clearinghouses are essential for trade confirmation and settlement. These interfaces validate transaction details, exchange confirmations, and settle trades.
Final Thoughts
The middle office plays a vital role in doubling up as a command center for trading systems operating in the capital markets. From orchestrating flawless trades, managing risks, and ensuring seamless transactions. a middle office system needs to be robust to enable automation, precise allocation, and customer communication. With cutting-edge technology, your firm can adapt, automate, and optimize for both profit and survival in this dynamic landscape. Get in touch with us to redefine your trade operations, shaping a more efficient, technologically strong future.