What Is An Order Management System?
An Order Management System (OMS) is a digital system designed to efficiently and economically carry out securities orders. It is commonly employed by brokers and dealers to handle orders for different types of securities while keeping tabs on each order’s status within the system.
How Does An Order Management System Work?
To initiate the purchase or sale of a security, a dealer must submit a trade order comprising several crucial details:
- The specific security involved is identified by its ticker symbol.
- The order type, such as buy or sell.
- The order’s size or quantity.
- Additional instructions for the order.
Traditionally, dealers execute trade orders through order management software. Many order management system systems utilize the Financial Information exchange (FIX) protocol, which is prevalent in securities markets and facilitates a significant portion of transactions.
Furthermore, the order management platform maintains a comprehensive record of both active and completed orders, ensuring transparency for all parties involved in securities transactions.
What Is The Difference between PMS (Portfolio Management System) And EMS (Execution Management System)?
| PMS | EMS |
| Hedge funds and other major buy-side investors rely on PMS for a holistic view of their market positions. | EMS is a subset of the order management system, focusing on responsiveness and facilitating time-critical transactions. |
| The order management system serves as a crucial element within the PMS, seamlessly integrated to facilitate trading activities. | EMS is particularly beneficial for day traders, as it supports rapid real-time decision-making and execution. |
| Order management system plays a pivotal role by translating asset allocation decisions into executable buy-side orders. | Despite the nuances, both the order management system and EMS share a core objective: executing trades based on the required market positions. |
| It ensures efficient order routing, execution, and tracking, enhancing the precision and speed of buy-side transactions. | Despite the nuances, both order management system and EMS share a core objective: executing trades based on the required market positions. |
| Despite the nuances, both the order management system and EMS share a core objective: executing trades based on the required market positions. | They work in tandem to streamline trade execution and optimize the investment process for different trading styles and strategies. |
Differences between Buy-side Order Management Systems And Sell-side Order Management Systems
User Role And Purpose
- Buy-side: Designed for institutional investors like asset management firms and hedge funds. Its primary focus is on managing investment portfolios, making purchase decisions, and optimizing asset allocation.
- Sell-side: Tailored for brokerage firms, market makers, and investment banks. Its main role is to facilitate order execution and trading activities on behalf of clients.
Order Flow Direction
- Buy-side: Manages orders initiated by the buy-side entity, which are typically related to purchasing and holding securities.
- Sell-side: Handles orders received from external clients, executing trades on their behalf, and often involves high-frequency trading strategies.
Complexity And Functionality
- Buy-side: Focuses on long-term investment strategies, portfolio optimization, and risk management, often requiring comprehensive analytics and reporting capabilities.
- Sell-side: Requires advanced trading functionalities, including algorithmic trading, real-time market data, and connectivity to multiple execution venues.
Client Relationships
- Buy-side: Establishes and maintains client relationships with external money managers, providing investment opportunities and portfolio management services.
- Sell-side: Acts as an intermediary between clients and the financial markets, executing orders on behalf of clients while maintaining a competitive edge.
Regulatory Compliance
- Buy-side: Emphasizes compliance with regulations related to portfolio management, risk assessment, and investor protection.
- Sell-side: Must adhere to regulations concerning trade execution, order routing, and market integrity, given its role in executing client orders.
What Are The Benefits of An Order Management System?
Enhanced Profitability
Traders experience a significant boost in profitability when they embrace an order management system. This powerful tool enables them to streamline their operations, effectively reducing operating expenses. By swiftly identifying high-performing trades and operations, traders can make informed decisions that contribute to increased profits.
Elevated Customer Care and Marketing
With an order management system in place, traders gain the upper hand in customer care and marketing strategies. The system facilitates seamless tracking of all customer trade queries, allowing for prompt and precise responses. This enhances the overall customer experience and fosters stronger client relationships.
Optimized Production
Order management systems empower traders to fine-tune their production techniques. By effortlessly tracking trade statistics and generating comprehensive reports, the system provides invaluable insights. Traders can closely monitor the performance of their operations and the efficiency of their production methods, leading to improved productivity.
Effective Risk Management
Managing risk becomes second nature with the assistance of an order management system. As each trade transaction is logged, the system employs a sophisticated risk management module. This invaluable tool enables traders to proactively halt unprofitable and potentially risky trades. By adhering to well-defined risk management objectives, traders can maximize profits while minimizing losses.
These benefits merely scratch the surface of what a trade order management system can offer. The adoption of such a system is not just advantageous; it is essential for traders aiming to make informed, intelligent decisions. Embracing this technology enhances the trading experience and equips traders with the tools they need to thrive in the dynamic world of finance.
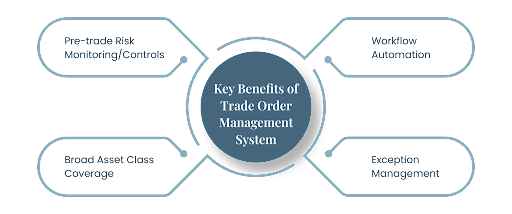
Key Features of An Order Management System
An order management system serves as a crucial tool for traders, enabling them to operate efficiently in the dynamic world of trading while addressing organizational challenges. It offers a range of essential features:
Multi-Asset Class And Order Type Support
An order management system should seamlessly handle multiple asset classes (stocks, bonds, derivatives, etc.) and various order types (market, limit, stop, etc.), catering to diverse trading strategies.
Risk Checks
Robust risk management tools and analysis are essential for real-time risk assessment, helping to prevent excessive exposure and mitigate trading risks effectively. Trading violations will be captured in a live blotter to enable compliance to research and approve or reject violations.
15c3-5 Risk Controls
Compliance with regulations like SEC Rule 15c3 is crucial. An order management system should offer features that aid in compliance and reporting. According to the rule, an order management system must provide thorough checks of the orders before market access, thereby not sending orders as naked or unfiltered. Also, ensure certain firm-level controls and stop erroneous orders from entering the market through specific logical filters.
Compliance Controls
Comprehensive compliance checks ensure that trades adhere to regulatory requirements and internal policies, reducing the risk of violations. Pre-trade compliance needs to be integrated with the order-raising workflows, including intuitive workflows for viewing rule usage and managing breaches. Automated pre-and post-trade compliance checks to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, investor mandates, and internal risk controls, speed the trading process, and free up staff to focus on exceptions.
Real-time Trade Monitoring
The trade blotter provides a real-time overview of trading activity, helping broker-dealers and traders stay informed and make timely decisions. The trade blotter is an important tool that can provide at a deeper level, the real-time status of the order, a view of the historical orders, pre-trade transaction costs, FIX messages received, and more.
FIX Connectivity
Support for FIX (Financial Information Exchange) protocol is essential for seamless communication with brokers and other trading partners. It enables secure and reliable access to a rapidly growing broker connectivity network with thousands of liquidity destinations across multiple asset classes and round-the-clock proactive support.
Smart Order Routing
Intelligent routing algorithms optimize order execution by selecting the best available venues, price over liquidity, etc., ensuring the best possible execution prices.
Fractional Order Trading
Most of the order management systems in the market now offer fractional trading capabilities, which have become much needed in recent years, making highly priced stocks more available to the investor segment who couldn’t previously afford to purchase their favorite stocks.
How Ionixx Can Help?
An order management system is a vital tool in the world of financial markets, serving as the backbone of efficient and effective securities trading. It streamlines the process of handling various types of securities orders, providing transparency and enhancing profitability for traders and investors. A high-performance order management solution is key to empowering modern-day broker-dealers who are chasing goals of trade order optimization and pre-trade compliance. Ionixx helps broker-dealers adapt to the changing capital markets landscape with its order management solutions, replete with features such as real-time account balances/ position updates and comprehensive reporting. Speak to our OMS solutions team today.