In digital finance, trading has a pivotal role to play. However, it is highly centralized, time-consuming, and cost-intensive because of high trading costs. All this is set to change with the rise of DEX, popularly known as decentralized exchanges. It promises freedom from the exclusive club, which is highly regulated and centralized. In the existing financial system, the rules are tweaked in favor of vested interests, and users have to pay hefty fees in many ways.
Overall, CEX has been designed in a way that puts common users at a disadvantage.
Unlike centralized exchanges, DEX is not an exclusive club of big boys that sets the rules of the game in their favor. Since its launch in 2014, its growth has been remarkable. According to a research paper by Science Direct, the trading volume on DEX has crossed USD150 billion in 2022.
This blog explores the evolution and history of decentralized exchanges.
What is DEX?
Think of it as an online marketplace without any big bank or middleman. You swap coins with other traders without paying considerable transaction costs. DEX puts in complete control of the game where the rules of the game are fair, transparent, and equitable. Decentralized exchanges are a critical part of the DeFi-based Web3 ecosystem.
A Brief Overview of Trustless Trading
Trust between two parties is the basis of a transaction in an existing financial system. However, this is often vague, which causes disputes between parties.
However, no centralized authority facilitates trust between parties in the trustless system. Smart contracts-based codes replace this trust. This is the central characteristic of blockchain-based cryptocurrency trading platforms.
According to Michigan Technology Law Review, being trustless is one of the vital characteristics of blockchain, as ‘trust’ is replaced by blockchain’s smart contracts protocol.
Evolution of Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
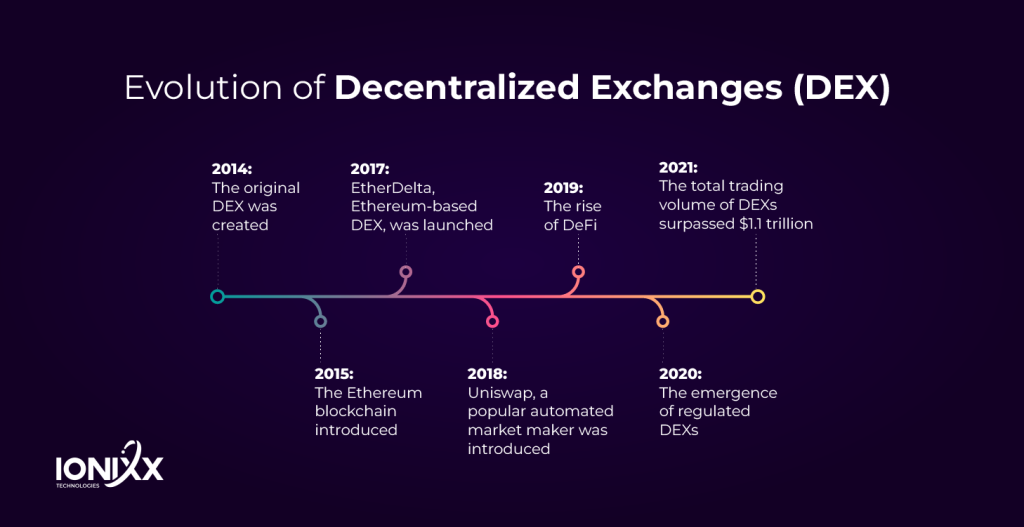
The genesis of crypto exchanges starts with the launch of Bitshares and NXT. Those were the early days of DEX evolution. They were popularly called Order Book DEX, allowing users to match the buy and sell orders directly. However, they suffered from many limitations.
Later, some prototypes came into being that addressed some of the shortcomings of Order Book DEX. Platforms like Mt. Gox simplified crypto trading. LocalBitcoins and Bisq were good examples of initial prototypes of the P2P Bitcoin exchange.
The Rise of Ethereum-Based DEX
Ethereum protocol fuelled the development of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), as the smart contracts functionality made creating many products like DApps possible.
However, no gaps still prevented DEX from offering many services. Creating a variety of digital tokens to meet specific use case needs was a hurdle. The development of ERC-20 tokens addressed this problem to a great extent.
Another challenge for Ethereum-backed DEXs was the inability to handle the large trading volumes. Blockchain developers solved this issue by including layer-two scaling solutions like Optimistic Rollups and ZK-Rollups.
DEX Beyond Ethereum Protocols
The subsequent growth stage emerged from the rise of DEX platforms beyond the Ethereum network. These platforms were based on different principles that addressed many limitations of Ethereum-based DEXs.
It empowered them to offer various services, such as crypto derivatives, spot trading, yield farming, analytics, and advanced order types, empowering traders to navigate the crypto market better.
Platforms like Binance, Cosmos, and Polkdot provided features comparable to existing CEX. The gap between DEX and CEX blurred. Each of these has distinct features. Let’s understand IT with some examples:
- Binance is an open-source, non-custodial, decentralized exchange that leverages the Binance-chain blockchain protocol. It utilizes TrustWallet, a form of non-custodial wallet.
- Cosmos operates on enabling the creation of independent, parallel blockchains known as zones. These zones accelerated transaction speed.
- Polkdot uses a different technology based on creating interoperable blockchains, also known as parachains.
Innovation in Critical to Next-Gen Growth
Nowadays, decentralized exchanges are migrating to Layer-2 solutions. Optimism and Arbitrum are good examples that address Ethereum’s scalability limitations and lower transaction fees. Platforms like Oasis and Secret Network offer privacy-preserving trading utilizing zero-knowledge proofs.
The introduction of Automated Market Making (AMM), powered with Uniswap blockchain protocol, set the stage for the next level of growth. It was a significant leap from the order book-based cryptocurrency exchanges, opening the possibilities of experimentation with different pool designs, fee structures, and token incentives.
AMM proved instrumental in the growth of decentralized exchanges in many ways, especially in building liquidity pools from user-deposited tokens.
Future Trajectory of Decentralized Exchanges
The future of Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) involves enhanced adoption, cross-chain compatibility, and integration with traditional finance.
Despite facing challenges related to liquidity, scalability, high transaction fees, and regulatory issues, DEXs have come a long way, eventually reaching a total trading volume of $1.1 trillion in 2021.
The future trajectory of DEXs will depend on various factors, such as how Layer 2 scaling solutions take shape, how the regulatory landscape evolves, and, most importantly, how blockchain developers address interoperability limitations.
Closing Thoughts
The evolution of DEX is an exciting chapter in the history of cryptocurrency. It has come a long way from merely being a concept to becoming a reality. As the crypto industry evolves, further innovation will make it more intuitive, user-friendly, and easier to use.
If you are looking to integrate web3 solutions for your business, get in touch with us.
[sticky_tab url=”https://bit.ly/42rVqiY” text=”Explore Our Web3 Solutions”]


