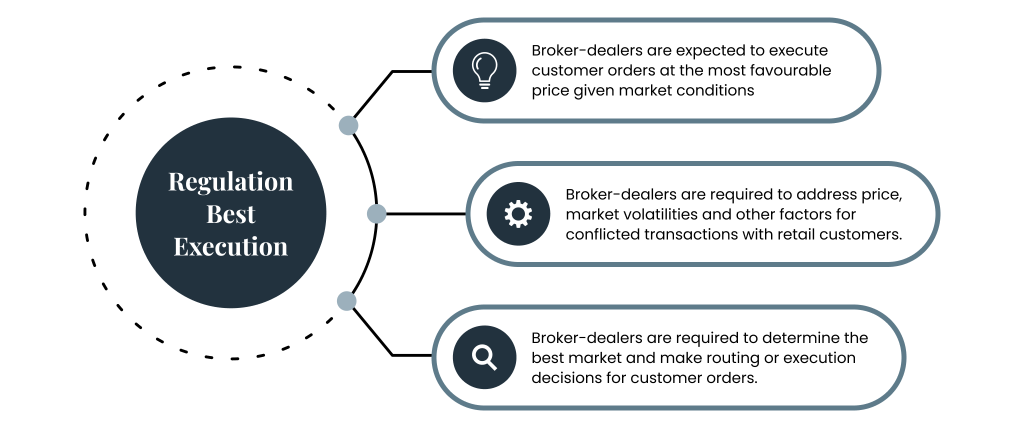
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) proposed Regulation Best Execution on December 14, 2022, to make sure that broker-dealers make a good-faith effort to find and give the best available market for their customers’ orders.
Regulation Best Execution
The SEC proposed this rule on Dec 14, 2022. The proposal would create a best execution standard for broker-dealers, government securities brokers, government security leaders, and municipality security brokers. It requires them to exercise reasonable diligence to identify the best market for a security and buy or sell in that market. So that the price they charge their customers is the “most favorable price” under the circumstances.
Regulation Best Execution at A Glance
The application of Regulation Best Execution encompasses a wide range of securities products, spanning equities, options, corporate and municipal bonds, government securities, and even “crypto asset securities.” Its provisions comprise
- Codification of a federal rules-based best execution standard (proposed Rule 1100 series) for brokers, dealers, government securities brokers, government securities dealers, and municipal securities dealers, including exceptions akin to current provisions.
- Mandate for broker-dealers to institute, sustain, and enforce written policies and procedures aligned with the best execution standard (proposed Rule 1101), with a limited exemption for introducing brokers (proposed Rule 1101(d)).
- Imposition of heightened policies and procedures for broker-dealers engaging in specific “conflicted transactions” with retail customers (proposed Rule 1101(b)).
- Requirement for broker-dealers to conduct quarterly evaluations of the execution quality of customer transactions (proposed Rule 1101(c)).
- Obligation for broker-dealers to conduct annual reviews of their best execution policies and procedures, accompanied by detailed reports of the assessment’s outcomes, presented to their boards of directors or equivalent governing bodies (proposed Rule 1102).
Common Challenges Broker-dealers Face with Regulation Best Execution Compliance
Because of this Regulation Best Execution, broker-dealers are facing many challenges and complexities in navigating the rule. The management of conflicted transactions adds further complexity, demanding transparent decision-making aligned with both regulations and client interests.
Fair Pricing with Market Maker:
Getting a good pricing strategy for a Broker-Dealer firm with a Market Maker can be quite a rare case scenario. Most of the Market Makers make huge profits from the wide bid-ask spreads that the investors are meant to enjoy. So for a Broker-Dealer to gain good Best Execution methods in providing to the investor, a fair pricing strategy is required with the Market Maker, so there is enough room for the investor for any advantage from price improvement.
High-Quality Market Data for TCA:
For a pre-trade or post-trade TCA reporting or analysis, the Broker-Dealer will need real-time of high-quality reference and market data. The TCA heavily banks on the data to provide the right kind of analytics that are crucial in decision-making for retail and institutional investors.
Technological controls:
The internal systems and operations of the Broker-Dealers related to execution order routing and other middle office functions need to be on par with the Best Execution practices. Ensuring proper methodologies and backend functionalities to support Best Execution is key to getting the best quality.
For example, getting a world-class OMS that has already built system controls for Best Ex supporting all asset classes, smart order routing (SOR), and having the fastest ATS are some of the tech aspects that Broker-Dealers need to emphasize in providing quality execution.
To comply with Regulation Best Execution, broker-dealers have to undergo a thorough compliance review of their practices for handling customer orders.
Broker-dealers who engage in conflicted transactions may also have to consider changes to their business models.
What are the Effective Practices to Comply with the Regulation Best Execution Rule?
Adherence to the Regulation Best Execution Rule is essential for transparency and investor trust. So, it is important for broker-dealers to adopt practices to ensure compliance and enhance the best execution outcomes.
Exception Reports: Helping companies meet their best execution obligations by using exception reports and surveillance reports.
PFOF (Payment for Order Flow) Review: This involves looking at how PFOF affects the order-routing process, including the following: any explicit or implicit contractual arrangement to send order flow to a third-party broker-dealer, whether it is per share or per order or it is based on the type of order, size of the order, type of customer, or market class of the security.
Risk-Based Reviews: Doing “regular and rigorous” reviews at least every three months, but depending on the business plan of the company.
Continuous Updates: Changing WSPs and best performance analyses to reflect changes in the account, the market, and the technology.
Why Regulation Best Execution?
The proposed Regulation Best Execution by the SEC aims to achieve several key objectives:
- Establish Best Execution Standard: To establish the best execution benchmark for broker-dealers, including brokers, dealers, government securities brokers, government securities dealers, and municipal securities dealers.
- Imposition of Policies and Procedures: Mandating broker-dealers to create, uphold, and enforce written policies and procedures designed to align with the best execution standard.
- Enhanced Guidelines for Conflicted Transactions: Requiring broker-dealers engaging in specific conflicted transactions with retail customers to implement more robust policies and procedures.
- Regular Transaction Execution Quality Review: Mandating broker-dealers to conduct quarterly assessments of the execution quality of customer transactions.
- Exemption for Qualifying Introducing Brokers: Exempting qualifying introducing brokers from certain requirements upon establishing, maintaining, and enforcing specified policies and procedures.
- Annual Best Execution Policies and Procedures Review: Requiring broker-dealers to conduct an annual review of their best execution policies and procedures. Additionally, they must present a detailed report outlining the results of this assessment to their boards of directors or equivalent governing bodies.
Why It Is Important To Comply with Regulation Best Execution?
Best execution requires broker-dealers to complete trades for their customers in a way that gives them the best possible terms. This duty comes from agency principles and personal duties in common law, and it is enforced by the antifraud parts of Federal securities laws. The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc.’s predecessor, the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc., made a rule called “best execution” in 1968. However, the SEC has never made a rule like this.
Robust consideration of execution opportunities by broker-dealers offers customers potential access to favorable terms. Hence, prioritizing optimal customer order execution holds paramount importance for both investors and the market, forming a crucial facet of investor protection. The Commission has consistently addressed the duty of best execution in its statements, and this initiative marks its inaugural proposal of regulations dedicated to addressing this duty.
How Can Broker-Dealers Effectively Prepare to Comply With Regulation Best Execution?
Broker-dealers can use these tactics to prepare for and meet the best execution requirements:
1. Finding Sources of Liquidity
Broker-dealers must have policies for identifying major liquidity sources. The proposed Rule 1101(a)(1)(ii) emphasizes identifying these sources but doesn’t specify a market quantity. According to proposed Rules 1101(a)(1)(i) and (ii), compliance entails assessing accessible information and identifying sources.
2. Assessing Business Size and Liquidity
The broker-dealer’s activities and customer order flow affect the identification of significant liquidity sources. A broker-dealer may discover liquidity sources using different marketplaces or market data depending on whether it accepts institutional or retail orders.
3. Effects on Liquidity Source Assessment
Assessing market information and finding liquidity sources involves several factors:
Trading characteristics: Security type impacts liquidity source assessment.
Market Transparency: The assessment procedure depends on the level of market transparency.
Market Accessibility: Costs and practicality of market connectedness affect decisions.
4. Market-Specific Considerations
For instance, a market with high connectivity or market data fees may lead the broker-dealer to assess information accessibility and liquidity prospects.
Broker-dealers can meet the best execution standards by developing thorough liquidity source identification policies. Broker-dealers can optimize execution and maintain compliance by considering their business, customer order flow, and market.
Conclusion
The SEC’s proposed Regulation Best Execution introduces transparency and trust into financial markets, aiming for standardized practices among broker-dealers. Challenges arise in adhering to rules on conflicted transactions and execution quality. To know more about the intricacies of the Regulation Best Execution, please read our extended version of this blog.